What is the Difference Between Hard Mold and Soft Mold?
Mold manufacturing plays a crucial role in various industries, from automotive to medical devices, electronics, and consumer products. Understanding the differences between hard mold and soft mold is essential for selecting the right molding solution for specific production needs. This article explores the key distinctions between hard molds and soft molds, their applications, advantages, and considerations for choosing the right one.
Hard Mold vs. Soft Mold: Key Differences
1. Material Composition
-
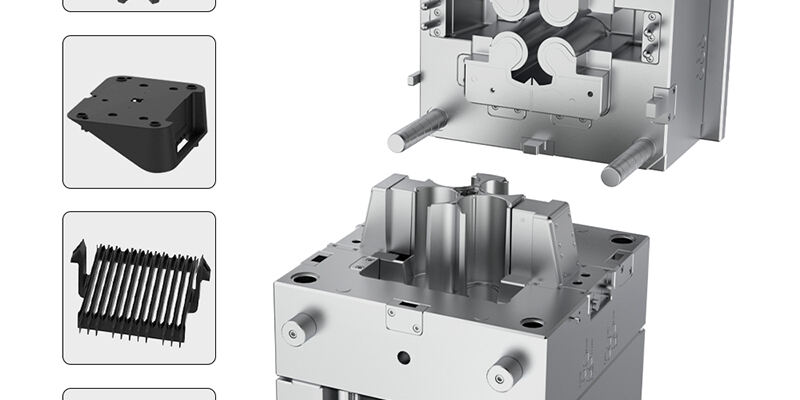
Hard Mold: Made from durable materials like hardened steel or high-grade aluminum, designed for long-term and high-volume production.
-
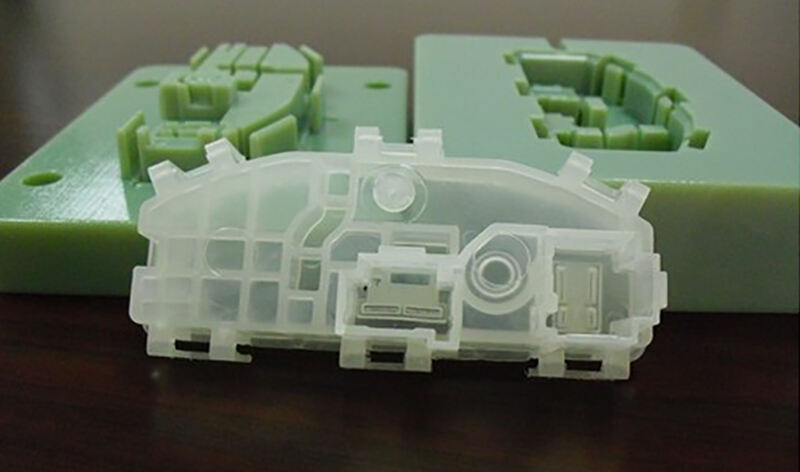
Soft Mold: Typically crafted from softer materials such as aluminum, epoxy, or pre-hardened steel, suitable for prototyping and low-volume production.
2. Durability and Lifespan
-
Hard Mold: Offers superior durability and can withstand hundreds of thousands to millions of injection cycles without significant wear.
-
Soft Mold: Has a limited lifespan, usually ranging from a few thousand to tens of thousands of cycles before requiring replacement.
3. Production Volume
-
Hard Mold: Ideal for large-scale production runs where consistency and longevity are critical.
-
Soft Mold: Best suited for short-run productions, prototyping, or situations where design modifications may be needed.
4. Cost and Lead Time
-
Hard Mold: More expensive to manufacture due to the high-quality materials and precision machining required. However, the cost per part is lower in high-volume runs.
-
Soft Mold: More cost-effective for initial tooling and has a shorter lead time, making it ideal for rapid prototyping or small-batch manufacturing.
5. Surface Finish and Precision
-
Hard Mold: Provides high precision and excellent surface finish, which is essential for complex and intricate designs.
-
Soft Mold: May have slight variations in precision and surface finish, but it is sufficient for many applications requiring quick turnaround.
Applications of Hard and Soft Molds
-
Hard Molds:
-
Mass production of plastic components
-
High-precision parts for medical, automotive, and aerospace industries
-
Consumer electronics requiring tight tolerances
-
-
Soft Molds:
-
Rapid prototyping and product testing
-
Low-volume specialty items
-
Market testing before committing to large-scale production
-
Choosing the Right Mold for Your Needs
Selecting between hard mold and soft mold depends on several factors, including budget, production volume, timeline, and product complexity. Companies like Topwell Moulding specialize in delivering tailored molding solutions, ensuring that clients receive the optimal mold type for their specific application.
Conclusion
Both hard molds and soft molds play vital roles in the manufacturing process, each serving distinct purposes. While hard molds offer durability and cost-effectiveness for high-volume production, soft molds provide flexibility and lower initial investment for prototyping and limited runs. Understanding these differences enables manufacturers to make informed decisions, optimizing efficiency and cost-effectiveness in their production processes.
For high-quality injection molding solutions, visit Topwell Moulding.
Comments
Post a Comment